In the labyrinthine landscape of human physiology, few molecules hold as much sway over our weight and metabolic equilibrium as leptin.
Discovered in the mid-1990s, this hormone, primarily originating from adipose tissue, has emerged as a linchpin in the body’s regulation of appetite and energy expenditure.
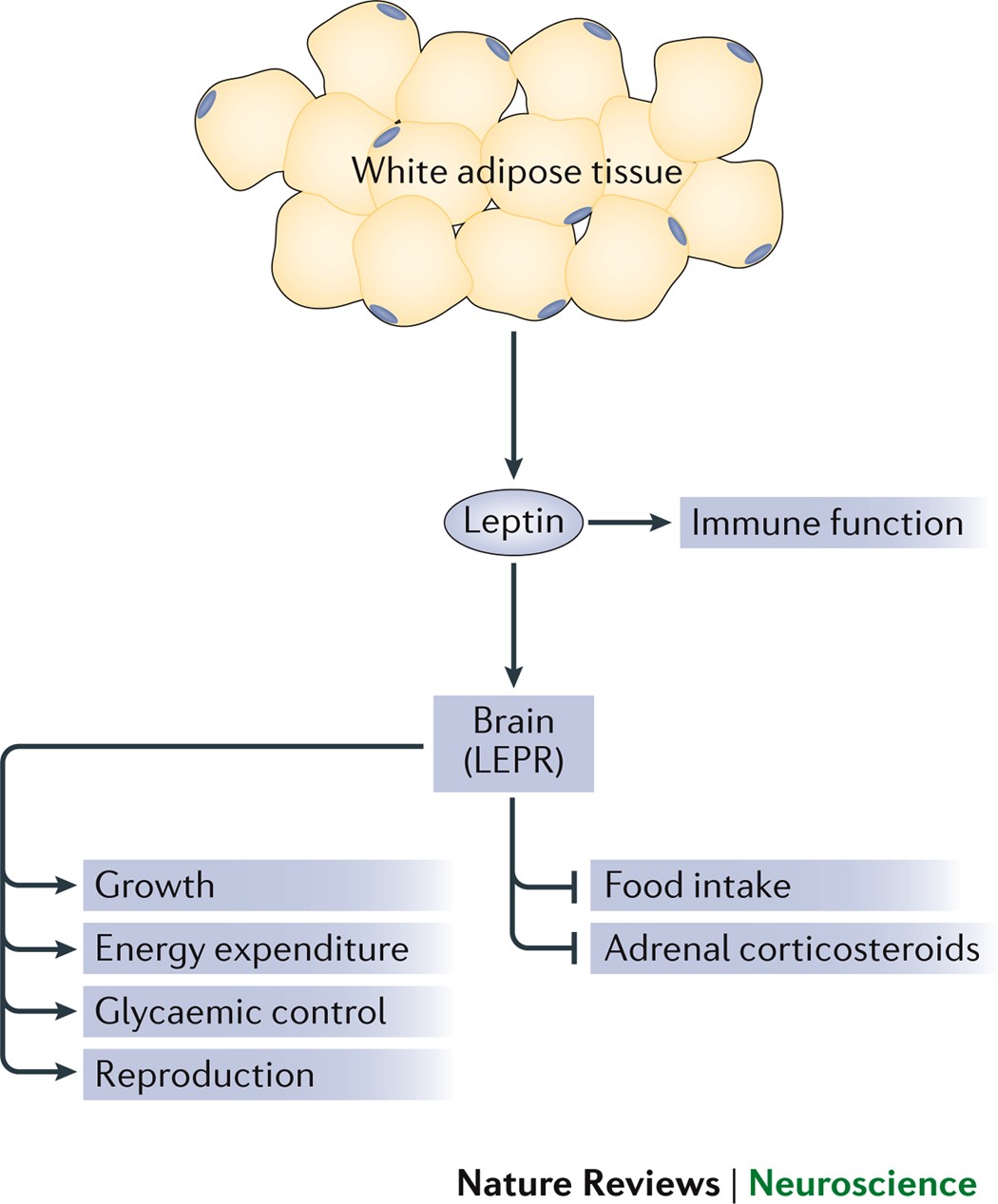
Leptin’s role in the intricate interplay between fat stores and brain functions has reshaped our comprehension of obesity and related metabolic disorders.
Derived from the Greek word “leptos,” meaning thin, leptin’s name mirrors its fundamental association with body composition.
Since its initial revelation, the importance of leptin has steadily grown, transcending its initial role as a satiety signal.
It now stands as a guardian of metabolic well-being, influencing not only our cravings but also our body’s capacity to manage and store energy.
In this article, we embark on a comprehensive journey through the world of leptin, unraveling its origins, functions, and the critical implications it holds for human health.
Through a blend of insightful paragraphs and structured listicles, we aim to elucidate the role of leptin in our body’s intricate dance with weight regulation.
Join us as we delve into the remarkable universe of leptin, uncovering secrets that may pave the way for groundbreaking advancements in obesity management and metabolic health.
Let’s Unravel the Wonders of Leptin
1. The Discovery of Leptin
Leptin, a pivotal hormone in the regulation of body weight, was unveiled to the scientific community in a groundbreaking discovery in 1994. This revelation emerged from rigorous research focused on unraveling the complexities of obesity in mice.
Scientists isolated a hormone secreted by fat cells, a molecule that would come to be known as leptin. Its name, derived from the Greek word “leptos,” meaning thin, reflects its fundamental association with body composition.
This seminal discovery marked a turning point in the understanding of weight regulation. For the first time, researchers had a tangible link between adipose tissue and the brain’s control of appetite and energy expenditure.
Leptin was revealed as a communicator, relaying vital information about the body’s energy stores to the brain. This signaling mechanism opened new vistas in the field of obesity research and paved the way for innovative approaches to tackle weight-related health challenges. Since its discovery, leptin has remained a beacon of hope in the quest for effective strategies to combat obesity and related metabolic disorders
2. Leptin as the Appetite Regulator
Leptin, the hormone secreted primarily by adipose tissue, exerts a profound influence on appetite regulation through intricate signaling mechanisms. Here are the key points highlighting its role as a vital appetite regulator:
- Satiety Signal: Leptin serves as a crucial satiety signal to the brain, specifically the hypothalamus, which plays a central role in appetite control.
- Direct Impact on Neurons: It directly interacts with specialized neurons in the hypothalamus, inhibiting hunger and promoting a feeling of fullness.
- Responsive to Fat Stores: Leptin levels are directly proportional to the amount of fat stored in the body. As fat stores increase, so do leptin levels, leading to a reduction in appetite.
- Feedback Loop: This hormone forms a feedback loop, allowing the body to regulate its energy balance. When fat stores decrease, leptin levels drop, signaling to the brain that energy reserves are low, subsequently increasing appetite.
- Influence on Metabolism: Beyond appetite, leptin also affects energy expenditure. Higher leptin levels lead to an increase in metabolic rate, ensuring that the body appropriately utilizes energy.
- Critical Developmental Role: Leptin is especially crucial during periods of rapid growth, such as infancy and adolescence, ensuring that energy stores are sufficient for proper development.
- Impact of Leptin Resistance: In cases of leptin resistance, a condition prevalent in obesity, the brain becomes less responsive to leptin’s signals. This can lead to a disruption in the body’s ability to regulate appetite effectively.
- Implications for Obesity Treatment: Understanding leptin’s role in appetite regulation has opened avenues for potential therapeutic interventions. Some studies explore ways to increase sensitivity to leptin signals, potentially aiding in weight management.
Leptin’s role as an appetite regulator underscores its significance in the broader context of metabolic health and weight management. This hormone stands as a key player in the complex symphony of physiological processes that govern our body’s energy balance.
3. Leptin Resistance and Obesity
Leptin resistance, a condition prevalent in obesity, is characterized by the brain’s reduced responsiveness to leptin’s signals. This phenomenon has profound implications for weight management and metabolic health. Here are key points outlining the relationship between leptin resistance and obesity:
- Definition and Mechanism: Leptin resistance occurs when there is an impaired ability of leptin to convey its satiety signals to the brain’s receptors, particularly in the hypothalamus.
- Vicious Cycle: As fat stores increase, so do leptin levels. In cases of leptin resistance, despite elevated leptin levels, the brain does not receive the proper signals of fullness, leading to continued overeating.
- Contributing Factors: Leptin resistance can be influenced by genetic predispositions, lifestyle factors (such as a high-fat diet), inflammation, and certain medical conditions.
- Role in Obesity Onset and Progression: Leptin resistance is not only a consequence of obesity but also a contributing factor. It can lead to an imbalance in energy intake and expenditure, exacerbating weight gain.
- Associations with Metabolic Syndrome: Leptin resistance is closely linked with metabolic syndrome, a cluster of conditions including high blood pressure, high blood sugar, excess body fat around the waist, and abnormal cholesterol levels.
- Challenges in Treatment: Leptin-based treatments for obesity have shown limited success, primarily due to the presence of leptin resistance. However, research continues in developing therapies that can enhance sensitivity to leptin signals.
- Potential Role of Lifestyle Interventions: Lifestyle modifications, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, may help improve leptin sensitivity and alleviate some of the effects of leptin resistance.
- Ongoing Research and Hope for Therapeutic Breakthroughs: Despite the challenges, ongoing research is focused on unraveling the complexities of leptin resistance. Promising avenues include targeting specific pathways and receptors to enhance responsiveness to leptin.
Understanding the intricate relationship between leptin resistance and obesity is crucial in developing effective strategies for weight management and metabolic health. It represents a significant area of exploration in the ongoing battle against obesity-related health challenges.
4. The Role of Leptin in Metabolism
Leptin, often recognized for its influence on appetite regulation, also exerts a profound impact on metabolism, encompassing a range of crucial physiological processes. Here, we explore how leptin plays a pivotal role in the intricate dance of metabolic functions.
- Regulation of Energy Expenditure: Leptin acts as a metabolic communicator, relaying information about the body’s fat stores to the brain. When leptin levels rise, it signals the brain that energy reserves are ample, resulting in an increase in energy expenditure.
- Modulation of Glucose Metabolism: Leptin exerts regulatory effects on glucose metabolism. It promotes insulin sensitivity, helping the body efficiently utilize glucose, thereby maintaining blood sugar levels within a healthy range.
- Influence on Lipid Metabolism: Leptin also plays a role in lipid metabolism. It aids in the breakdown of triglycerides stored in adipose tissue, ensuring a steady supply of fatty acids for energy production.
- Impact on Thermogenesis: Leptin contributes to thermogenesis, the process by which the body generates heat. This is essential for maintaining a stable body temperature and supporting metabolic functions.
- Regulation of Reproductive Functions: Leptin levels influence reproductive functions. In cases of low body fat, which leads to decreased leptin levels, reproductive processes may be compromised, highlighting the hormone’s importance in fertility.
- Crucial during Growth Phases: Leptin is particularly vital during periods of rapid growth, such as infancy and adolescence. It ensures that sufficient energy reserves are available for the body’s developmental needs.
- Metabolic Health and Disease: Imbalances in leptin levels or responsiveness can lead to metabolic disorders. Leptin resistance, for instance, is associated with obesity and metabolic syndrome.
leptin’s role in metabolism extends far beyond its appetite-regulating functions. It is a multifaceted hormone that intricately governs energy expenditure, glucose and lipid metabolism, thermogenesis, and even reproductive processes. Understanding these facets of leptin’s influence on metabolism provides valuable insights into the broader landscape of metabolic health and offers potential avenues for interventions in conditions related to metabolic dysregulation.
Conclusion
In the realm of weight regulation, leptin stands as a beacon of hope for understanding and managing obesity. Its intricate interplay with the brain and metabolic processes underscores its significance in maintaining a healthy body weight.
However, the prevalence of leptin resistance in obese individuals highlights the complexities of this system. Ongoing research aims to unravel the mysteries surrounding leptin and develop innovative approaches to combat obesity and related metabolic disorders.
As we continue to delve deeper into the realm of hormones and their impact on our health, leptin remains a focal point of investigation. By harnessing the knowledge surrounding this remarkable hormone, we inch closer to a future where effective strategies for weight management and overall metabolic health are within reach.